The Roman Empire
The idea of growing plants in ecologically controlled areas has been around since Roman times. The Roman emperor Tiberius was very fond of cucumbers and ate one piece every day. Roman gardeners developed their own system of year-round cultivation of cucumbers in order to receive fresh vegetables for the emperor’s table every day. The cucumbers were planted in the ground, which was in the carts. From that moment, the history of the creation of greenhouses began. These carts were taken out in the sun every morning and rolled into a warm room in the evening in order to keep them warm at night.
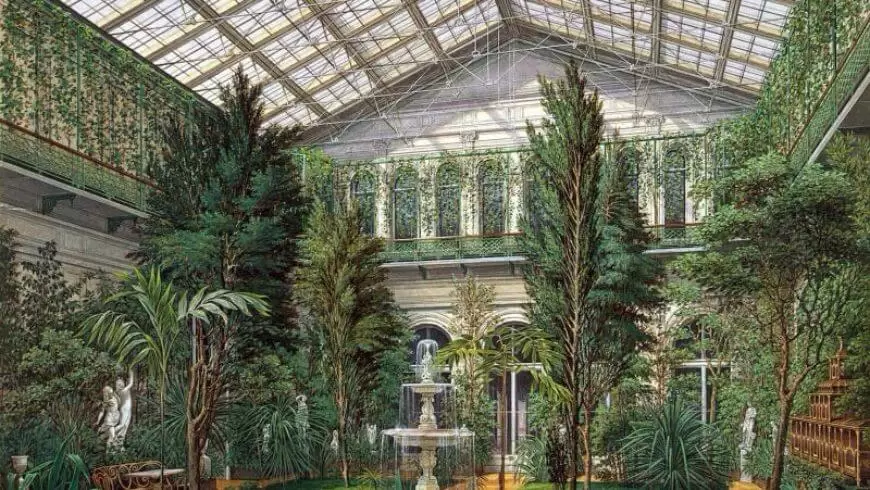 The beauty of the winter gardens of ancient Rome
The beauty of the winter gardens of ancient Rome
In the 13th century, greenhouses were built in Italy to house exotic plants that researchers brought back from the tropics. The name Botanical Garden also originated from there. “Active” buildings, in which it became possible to manually adjust the temperature, appeared much later. The first mentions date back to 1450. In Korea, a greenhouse was developed, the description of which contains the ability to adjust temperature and humidity for different plants and crops. Joseon Dynasty records contain descriptions of tangerine trees growing in Korean traditional construction during the winter with a heating system installed.

House of the sun, vegetarian
The predecessors of modern greenhouses also appeared in Holland and then in England in the 17th century. Such structures required tremendous efforts to prepare the structure for the night and for the winter period. Serious problems arose in providing a balanced microclimate and required temperature. Holland today hosts the largest greenhouses in the world, some of which are so large that they are capable of producing millions of flowers and vegetables every year.
The French called their first “plant houses” Orangeries, as they were built to protect orange trees from frost. French botanist Charles L. Bonaparte is often credited with building the first near-modern greenhouse in Leiden. Experiments with greenhouse design continued throughout Europe throughout the 17th century. The greenhouse in the Palace of Versailles was huge for those times. It was 150 meters long, with a width and height of 13 and 14 meters, respectively. In Japan, the first greenhouse appeared in 1880. It was built by a British herb exporter.
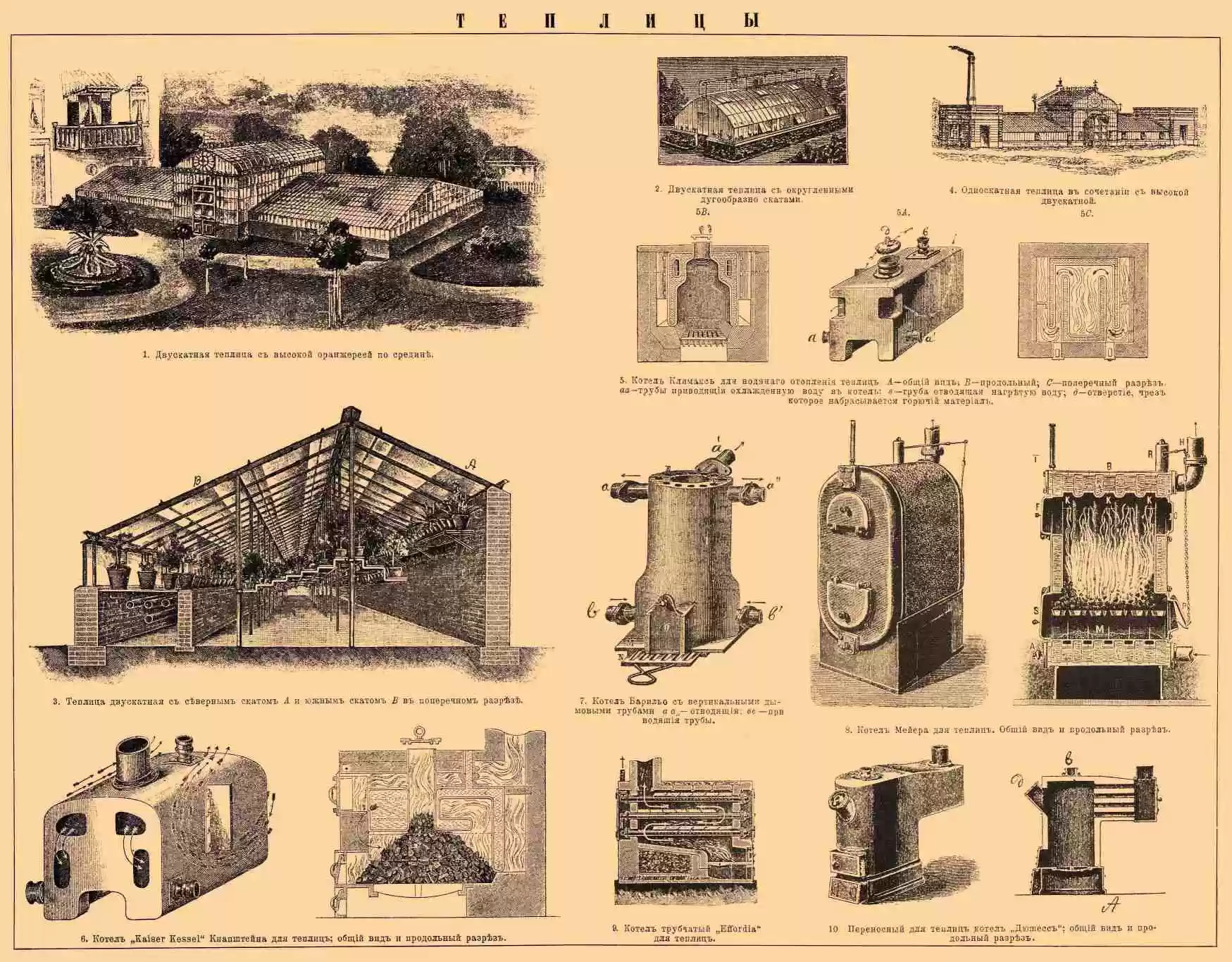 Greenhouses in Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary
Greenhouses in Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary
Nowadays Greenhouses History
Numerous greenhouses have been around since the 1960s, when plastic sheeting became widely available. Such greenhouses were made of aluminum and galvanized steel profiles or even just PVC pipes, since the costs of such a structure were low. This led to greenhouses being built on small farms and garden plots. The strength of the polyethylene film increased over time, and in 1970 UV protection was added to it, which dramatically increased the life of the film from 1 year to 5 years.
Since the 80s of the last century, modern structures have appeared, equipped with heating, additional lighting and systems for maintaining the required microclimate. The number of types of coverage has also expanded. In addition to film, materials such as glass and cellular polycarbonate are actively used in greenhouses.
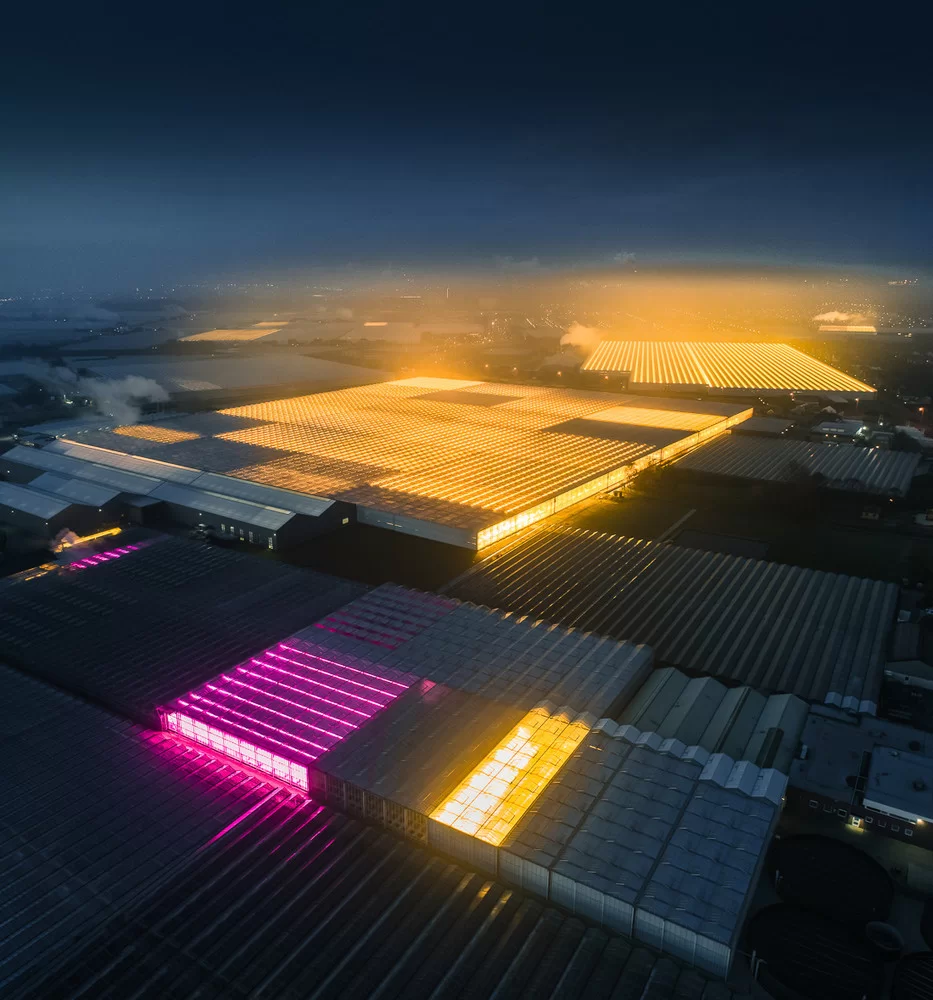 Greenhouses in the Netherlands
Greenhouses in the Netherlands
Progress does not stand still, greenhouse structures are constantly being improved. New materials and technologies are being introduced. Today there is a huge selection of greenhouses for different tastes and financial capabilities. It remains only to make this choice.







